In the dynamic landscape of virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), organizations are constantly seeking innovative solutions to enhance user experience, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. One such transition that holds immense potential is migrating from VMware Horizon (on-premises VDI) to Apporto’s Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS).
Given the ongoing turmoil and uncertain future created by the Broadcom acquisition, there is no better time to consider a switch away from Horizon.
This article will guide you through the seamless migration process, outlining key benefits and considerations for a successful transition. We offer two different migration options, each with a simple-to-follow migration path.
Why Perform a VMware Migration?
1. Definition and Benefits of Virtual Machine Migration
Virtual machine migration is the process of transferring a VM from one host to another while preserving its configuration, data, and applications. This process offers several significant benefits:
- Improved Resource Utilization and Allocation: By redistributing workloads, VM migration helps in balancing resource usage across multiple hosts, ensuring optimal performance.
- Enhanced Performance and Scalability: Migrating VMs allows for better load balancing and scalability, accommodating growth and changing demands without compromising performance.
- Reduced Downtime and Increased Availability: VM migration minimizes downtime by enabling maintenance and upgrades without interrupting services, thus ensuring higher availability.
- Simplified Management and Maintenance: The ability to move VMs between hosts simplifies the management of virtualized environments, making maintenance tasks more straightforward.
- Increased Flexibility and Agility: VM migration provides the flexibility to adapt to changing business needs, allowing for quick responses to new opportunities or challenges.
2. Importance of VM Migration in Virtualized Environments
In virtualized environments, VM migration is indispensable for several reasons:
- Optimize Resource Allocation and Utilization: By dynamically moving VMs, organizations can ensure that resources are used efficiently, avoiding bottlenecks and underutilization.
- Improve Performance and Scalability: VM migration supports load balancing and scalability, enabling systems to handle increased workloads seamlessly.
- Reduce Downtime and Increase Availability: Maintenance and upgrades can be performed with minimal disruption, ensuring continuous availability of services.
- Simplify Management and Maintenance: The ability to migrate VMs simplifies the overall management of virtualized environments, making it easier to maintain and update systems.
- Increase Flexibility and Agility: VM migration allows organizations to quickly adapt to changing requirements, providing the agility needed in today’s fast-paced business landscape.
3. Types of VM Migration: Live, Cold, and Hybrid
There are three primary types of VM migration, each with its own process and benefits:
- Live Migration: This involves moving a VM from one host to another while it is still running. Live migration ensures minimal downtime, making it ideal for critical applications that require continuous availability.
- Cold Migration: In this type, the VM is shut down before being moved to a new host and then restarted. Cold migration is typically used when live migration is not feasible or when significant changes to the VM’s configuration are required.
- Hybrid Migration: Combining elements of both live and cold migration, hybrid migration involves moving the VM while it is still running but with some planned downtime. This approach balances the need for minimal disruption with the practicalities of certain migration scenarios.
Preparing for Migration
Before embarking on the migration process, it is crucial to thoroughly assess migration readiness and meticulously plan each step. Proper preparation ensures a smooth transition and minimizes potential disruptions.
1. Assessing Migration Readiness and Planning
To ensure a successful migration, organizations should:
- Evaluate the Current Virtualization Environment: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the existing virtualization setup to identify any potential challenges or limitations that may impact the migration.
- Assess VM Compatibility: Verify that the VMs are compatible with the target host or platform, ensuring that all necessary configurations and dependencies are met.
- Plan the Migration Process: Develop a detailed migration plan that outlines the order of VM migration, expected downtime, and resource allocation. This plan should also include timelines and milestones to track progress.
- Develop a Contingency Plan: Prepare for potential issues by creating a contingency plan that addresses possible challenges and outlines steps to mitigate risks during the migration process.
By carefully planning and preparing for VM migration, organizations can ensure a smooth and successful transition that minimizes downtime and disruption to business operations. This proactive approach not only enhances the efficiency of the migration process but also ensures that the migrated VMs continue to perform optimally in their new environment.
Option 1 – DaaS with Virtual Machines
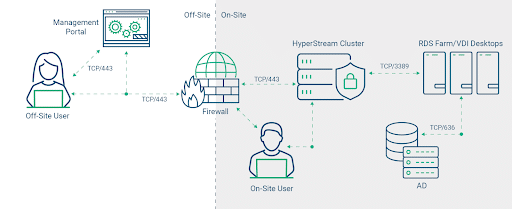
There has never been a better time to move to the cloud and execute a cloud-smart strategy. Leveraging the latest cloud technologies and cloud environments, Apporto makes DaaS incredibly easy with our fully managed service.
These cloud environments facilitate VM migrations between various platforms, including on-premise systems and data centers, enhancing manageability and cost optimization. We handle all of the heavy lifting so that you can focus on strategic projects and the business needs of your organization.
What You Keep vs. What You Can Discard
What You Keep | What You Can Discard |
|---|---|
Software Licensing | Connection Servers |
vCenter* | Unified Access Gateway
|
Horizon Edge Gateway
| |
Enrollment Server
| |
App Volumes Manager
| |
Horizon Licensing
| |
App Volumes Licensing
| |
VDA Licensing (MS)
|
*If used for other workloads
As shown, moving to Apporto’s DaaS platform can dramatically simplify your on-premise infrastructure and will help increase your security posture, as Apporto doesn’t require the plethora of firewall rules required by Horizon.
With the Apporto DaaS platform, migration couldn’t be simpler. Size your environment, order a subscription, and we’ll do the rest.
Of course, we keep you in the loop every step of the way and never lock you out of making changes should you need or want to. Flexibility is one of the key benefits you’ll enjoy with Apporto.
We understand that cloud-hosted DaaS isn’t for everyone. We also offer a hybrid DaaS option, where the majority of the infrastructure will still run on-premises.
Additionally, VMware vCenter Converter can be used to transform physical machines into VMware virtual machines and facilitate migrations between hosts and data centers.
Option 2 – Hybrid DaaS in Hybrid Cloud Environments
If you’re happy with your vSphere environment and there’s still life in your hardware, leave it in place and deploy Apporto instead. This gives you multiple advantages:
- Continue using existing hardware where you’ve already invested, utilizing your physical server as a foundation for hosting multiple virtual machines.
- Built-in cloud migration pathway if your future plans include cloud hosting.
- Cloud bursting and disaster recovery capabilities for additional flexibility.
What You Keep vs. What You Can Discard
What You Keep | What You Can Discard |
|---|---|
Software Licensing | Connection Servers |
vCenter* | Unified Access Gateway
|
Server Hardware
| Horizon Edge Gateway
|
Gold Images
| Enrollment Server
|
VDA Licensing (MS)
| App Volumes Manager
|
Horizon Licensing
| |
App Volumes Licensing
|
With our hybrid DaaS deployment, nearly everything runs on-premises and stays within your control. Our management portal stays cloud-hosted, but that’s it.
- Re-use your Gold Images
- Deploy your own cyber protection
- Scale your hardware however you want
The VMware environment offers robust capabilities for managing virtual machines and seamlessly migrating workloads to cloud platforms.
Key Benefits of Apporto DaaS/Hybrid DaaS
1. Cost-Efficiency
Apporto eliminates the need for extensive hardware investments and maintenance costs associated with on-premises solutions. This cost-effective model allows businesses to allocate resources more strategically.
Additionally, during data migration from physical to virtual systems or to cloud infrastructures, it is crucial to use reliable tools and strategies to ensure safe and efficient data transfer.
2. Improved Accessibility
DaaS provides users with any-time, anywhere access to desktop environments, enhancing collaboration and productivity. This is particularly beneficial for remote or mobile teams. The only requirements are an Internet connection and an HTML5-compatible browser.
Virtualization platforms enable users to create and manage multiple virtual machines on a single physical machine, enhancing efficiency, scalability, and resource management in IT environments.
3. Scalability with VM Migration
Apporto’s DaaS scales effortlessly to accommodate the growth of your organization. Whether you’re expanding your team or adopting new technologies, the platform adapts without compromising performance.
4. Security in Data Centers
Following industry best practices for zero-trust and leveraging multiple layers of protection and detection, Apporto’s DaaS platform is safe and secure, without compromising user experience or performance.
The VMware migration tool is crucial for P2V and V2V migrations, playing a significant role in efficiently managing data transfer during these upgrades.
5. Simplicity
Just three components, all managed from an intuitive web console—Apporto couldn’t be simpler to deploy and manage.
Conclusion
Whether your organization is executing a cloud migration strategy or just looking for a VMware Horizon alternative, there are multiple options available with Apporto.
As a leader in cloud-based virtual desktop solutions, Apporto is at the vanguard of facilitating remote work and learning. Recognized in Gartner’s 2023 Magic Quadrant for DaaS, Apporto is dedicated to providing secure, scalable, and high-performance computing environments that meet the demands of today’s dynamic digital ecosystem.
Additionally, tools like Faddom and vMotion play a crucial role in optimizing VMware migrations and minimizing risks by mapping dependencies and enhancing performance during the migration process.