Best Ways to Achieve 100% Endpoint Compliance
IT professionals understand that securing their internal systems and data starts with securing the endpoints that their various user groups utilize for daily tasks. But with a shift in the landscape to a more mobile, hybrid, and remote workforce, how best to accomplish the target of 100% compliance on endpoints?
There has been a clear progression of management systems over time from System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) to virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) to desktops-as-a-service (DaaS). Each has benefits and drawbacks, so let’s dig in.
SCCM
Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) is a comprehensive management tool designed to help administrators deploy, manage, and monitor devices and applications in an enterprise environment. It provides a centralized platform for IT professionals to automate various tasks related to software deployment, patch management, operating system deployment, and system updates.
Key Features and Functions:
Software Deployment: SCCM enables administrators to efficiently deploy software applications across multiple devices within an organization. It supports automated software installation, remote installation, and deployment targeting based on user or device-specific criteria.
Patch Management: SCCM helps administrators keep the software and operating systems on devices up to date by managing and deploying patches and updates. It allows for patching both Microsoft and third-party applications, ensuring security and stability across the network.
Operating System Deployment: SCCM facilitates the automated deployment of operating systems to new or existing devices. Administrators can create standardized OS images, customize configurations, and remotely install the OS on multiple devices simultaneously.
Inventory and Asset Management: SCCM provides comprehensive inventory and asset management capabilities, allowing administrators to track and manage hardware and software assets across the organization. It collects detailed information about devices, software installations, and hardware configurations.
Endpoint Protection: SCCM integrates with Microsoft Defender Antivirus to provide endpoint protection features. Administrators can centrally manage antivirus policies, monitor protection status, and respond to security threats.
Reporting and Monitoring: SCCM offers reporting and monitoring tools to gather insights into device and application health, compliance, and usage. It provides real-time monitoring and generates reports that help administrators make informed decisions.
Challenges and Drawbacks:
While SCCM does a great job with most devices, there are a few areas that can be challenging and potentially block the achievement of 100% compliance.
Complexity: SCCM is a feature-rich and highly configurable tool, which can lead to complexity in its implementation and management. Setting up SCCM requires careful planning, expertise, and familiarity with its various components and configurations.
Learning Curve: Due to its complexity, SCCM has a steep learning curve for administrators who are new to the tool. Acquiring the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively utilize SCCM may take time and training.
Infrastructure Requirements: SCCM relies on a robust infrastructure to operate efficiently. It requires dedicated server resources, such as database servers, distribution points, and management points. Organizations need to allocate the necessary hardware, network bandwidth, and storage capacity to support SCCM effectively.
Scalability and Performance: Large-scale deployments or managing a vast number of devices can strain the performance of SCCM infrastructure. Ensuring scalability and optimal performance may require careful monitoring, tuning, and additional hardware resources.
Software Compatibility: SCCM primarily focuses on managing Microsoft-based systems and applications. While it supports third-party software deployments, ensuring compatibility and smooth integration with all applications can be challenging. Some third-party applications may require additional customization or workarounds for effective management.
Overhead and Maintenance: SCCM requires regular maintenance tasks, such as software updates, database maintenance, and distribution point management. These activities may require dedicated resources and can consume time and effort.
Add to the above, the robust knowledge of internal device driver management across many manufacturers and models that is required. And, finally, in the new remote work landscape, SCCM only works with devices it can connect to. Offline or unreachable devices will not receive critical updates and patches.

As illustrated above, the total cost of ownership using SCCM is fairly reasonable but the effort required to achieve 100% endpoint compliance is high.
VDI
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that enables the delivery of desktop environments to end-users from a centralized server or cloud infrastructure. Instead of running applications and storing data on individual physical devices, VDI allows users to access a virtual desktop from any device with an internet connection.
Benefits of VDI:
Centralized Desktop Management: VDI centralizes desktop management, allowing administrators to deploy, configure, and update desktop environments from a single location. This simplifies IT tasks, reduces maintenance efforts, and ensures consistent configurations across all virtual desktops.
Remote Access and Mobility: VDI provides remote access to desktops, enabling users to access their virtual desktops and applications from anywhere, using various devices like laptops, tablets, or thin clients. This enhances productivity and facilitates mobile and remote work scenarios.
Improved Security: With VDI, sensitive data remains stored in the data center or cloud infrastructure, rather than on individual devices. This helps reduce the risk of data loss or theft from lost or stolen devices. Centralized security policies and controls can be implemented to protect virtual desktops and data.
Hardware Utilization: VDI allows for better utilization of hardware resources. Multiple virtual desktops can run on a single physical server, reducing the overall hardware requirements and energy consumption. This can result in cost savings and improved resource efficiency.
Streamlined Application Deployment: Applications can be installed and managed centrally in a VDI environment, reducing the complexities of application management across multiple endpoints. Administrators can easily update and deploy applications to all virtual desktops simultaneously, ensuring consistency and simplifying maintenance.
Enhanced Disaster Recovery: VDI environments can be backed up and replicated, making disaster recovery easier and more efficient. In case of hardware failures or other disruptions, users can quickly switch to alternative virtual desktops without significant downtime.
User Experience and Flexibility: VDI provides a consistent user experience across different devices, as users can access their personalized virtual desktop environment from any compatible endpoint. Users can easily switch devices without interrupting their work and have the flexibility to customize their virtual desktop to suit their preferences.
Challenges and drawbacks
The overall intent of VDI was to overcome the drawbacks of using an endpoint management tool like SCCM, however, there are some new challenges that must be taken into consideration.
Infrastructure Complexity: Implementing and managing a VDI infrastructure can be complex and resource-intensive. It requires robust server hardware, storage systems, and networking infrastructure to support the virtual desktops and ensure optimal performance. Organizations need to invest in the right infrastructure and have skilled IT personnel to handle the complexities.
Cost Considerations: VDI can involve significant upfront costs, including hardware, software licenses, virtualization technology, and storage infrastructure. Additionally, ongoing operational costs such as maintenance, upgrades, and support should be factored in. Organizations need to evaluate the total cost of ownership and determine if the benefits justify the investment.
Scalability and Performance: Scaling a VDI environment to accommodate a large number of users or handle peak workloads can be challenging. Ensuring adequate server resources, network bandwidth, and storage capacity are critical for maintaining performance and responsiveness. Organizations need to plan for scalability and regularly monitor and optimize the infrastructure.
User Experience: While VDI aims to provide a consistent user experience, factors like network connectivity, latency, and device capabilities can impact performance. In remote or low-bandwidth scenarios, users may experience lag or reduced functionality. Ensuring a satisfactory user experience across different devices and locations can require careful planning and optimization.
Application Compatibility: Certain applications may not be compatible with a virtualized environment or may require specific configurations. Graphics-intensive applications, legacy software, or applications with hardware dependencies can present challenges in VDI deployments. Compatibility testing and potential workarounds may be needed to ensure smooth application delivery.
Network Bandwidth Requirements: VDI heavily relies on network connectivity to deliver virtual desktops and transmit data between the server and endpoints. Bandwidth requirements can be significant, especially during peak usage times or when multimedia content is involved. Adequate network capacity and proper network design are crucial to prevent performance bottlenecks.
Data Security and Compliance: While VDI can enhance security by centralizing data and applications, it also introduces new security considerations. Securing the virtual desktop infrastructure, protecting data during transmission, and ensuring compliance with regulations require proper planning and implementation of security measures, including access controls, encryption, and monitoring.
While the benefit of centralized management and nearly immediate compliance with virtual desktops is appealing, the total cost of ownership (TCO) is a huge detractor for most companies.
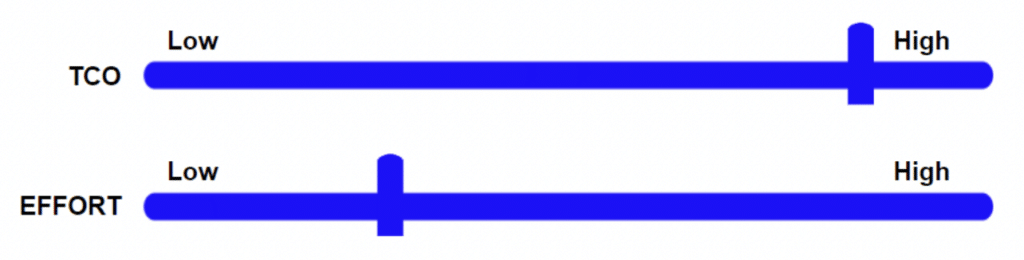
Here we can see that achieving 100% compliance with VDI requires a fairly low effort, however, the total cost of ownership is probably the highest of all solutions.
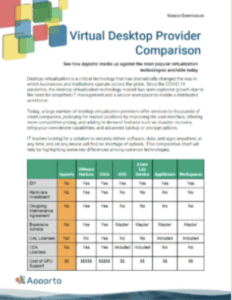
Virtual Desktop Provider Comparison
DaaS
Desktops-as-a-Service (DaaS) is a cloud computing model that delivers virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) from a service provider to end-users over the internet. In DaaS, the virtual desktops and associated applications are hosted and managed in the cloud, eliminating the need for organizations to deploy and maintain their own VDI infrastructure.
Key Features and Benefits:
Cloud-based Virtual Desktops: DaaS provides virtual desktops that run in the cloud, allowing end-users to access their desktop environments from various devices, including laptops, tablets, and thin clients. The virtual desktops are hosted and managed by a third-party service provider, relieving organizations of the infrastructure and management responsibilities.
Pay-as-you-go Model: DaaS typically follows a subscription-based or pay-as-you-go pricing model. Organizations pay for the virtual desktops and services they consume on a per-user or per-month basis. This offers flexibility and scalability as organizations can easily scale up or down based on their needs without upfront capital investments.
Outsourced Infrastructure Management: With DaaS, the service provider handles the management and maintenance of the virtual desktop infrastructure, including server hardware, storage, networking, and software updates. This frees up IT resources and reduces the burden of infrastructure management for organizations.
Anywhere, Anytime Access: DaaS enables users to access their virtual desktops from anywhere with an internet connection. Users can log in and securely access their personalized desktop environment, applications, and data from different devices, facilitating remote work, mobile productivity, and collaboration.
Simplified Deployment and Management: DaaS simplifies the deployment and management of virtual desktops. Organizations can quickly provision new desktop instances, manage user access and permissions, and deploy applications centrally through an administrative portal. This streamlines IT operations and reduces the time and effort required for desktop management.
Enhanced Security and Data Protection: DaaS offers built-in security features and data protection mechanisms. Data resides in the cloud infrastructure, reducing the risk of data loss from lost or stolen devices. Service providers implement security measures such as access controls, data encryption, and backup solutions to ensure the security and integrity of virtual desktops and user data.
High Availability and Disaster Recovery: DaaS providers typically offer high availability and redundancy in their infrastructure, ensuring that virtual desktops are accessible and reliable. In case of hardware failures or disruptions, service providers maintain backups and implement disaster recovery measures to minimize downtime and ensure business continuity.
Compatibility and Application Support: DaaS supports a wide range of applications, including both standard and specialized software. Compatibility testing and application packaging are typically performed by the service provider to ensure smooth application delivery. Users can access their familiar applications and tools without compatibility concerns.
Potential Drawbacks:
Internet Connectivity Dependency: DaaS heavily relies on internet connectivity for users to access their virtual desktops. Users in areas with limited or unreliable internet connectivity may experience disruptions or reduced performance. Downtime or network outages can prevent users from accessing their virtual desktops until connectivity is restored.
Performance and Latency: The performance of DaaS is influenced by network latency and bandwidth. Users accessing virtual desktops from remote locations or over long distances may experience latency or sluggishness, especially when working with resource-intensive applications or multimedia content. Optimizing network connections and selecting geographically closer data centers can help mitigate this issue.
Vendor Dependency: Adopting DaaS means relying on a third-party service provider for the infrastructure and management of virtual desktops. Organizations should carefully choose a reputable provider and evaluate their track record, service-level agreements (SLAs), and support capabilities. Vendor lock-in and the potential risks associated with service provider changes should also be considered.
Application Compatibility and Performance: Some applications, especially those with specialized hardware requirements or specific integration needs, may not perform optimally in a DaaS environment. Compatibility testing and performance evaluation should be conducted to ensure that critical applications meet the required performance levels and functionality in a virtualized environment.
Here again, we see the evolution of delivery and compliance from on-premises VDI to DaaS where the overall TCO is lowered.

However, there is still a large learning curve required to achieve compliance and more importantly protect company data and systems from external threats.
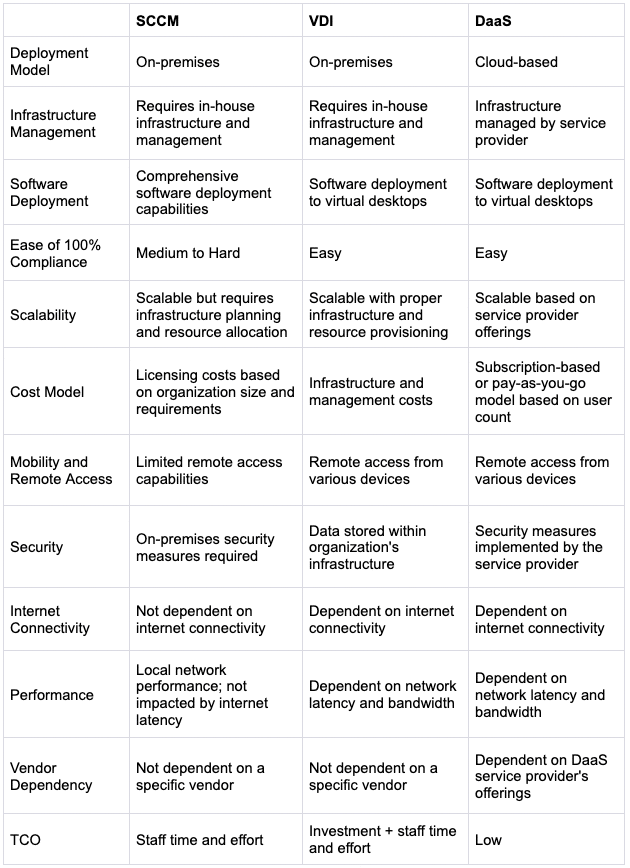
Comparison Chart
Meet Apporto
Apporto is a fully managed cloud-based virtual desktop solution that enables users to access their desktop applications and files from any device with an internet connection and a modern browser. It allows organizations to provide a centralized and secure desktop environment to their users without the need for expensive hardware or infrastructure.
One of the key benefits of Apporto is that it eliminates the need for users to install and manage their own software and hardware. It also provides a high level of flexibility, as users can access their virtual desktops from anywhere, at any time, and on any device. Additionally, Apporto offers enhanced security features like best practices for zero-trust, least privilege access, and admin-managed Network Objects.
Users will enjoy a best-in-class user experience for both performance and ease of use, ensuring anywhere access and increased productivity.
Apporto offers a range of pricing plans, including options for educational institutions, businesses, and individuals. It is also easy to set up and use, with no special technical skills required.

Because Apporto is a fully managed service, the effort required to achieve 100% compliance is nearly zero and the cost optimization included with the platform makes total cost of ownership the lowest among all solutions.
As we can see, there is a clear evolution of approach for achieving endpoint compliance from SCCM to VDI to DaaS, with the final step being to Apporto. We simplify cloud desktops.